目录
一、准备
建表与数据准备:
# 建表
create table department(
id int,name varchar(20)
);
create table employee(
id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',age int,dep_id int
);
# 插入数据
insert into department values
(200,'技术'),(201,'人力资源'),(202,'销售'),(203,'运营');
insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('nick','male',18,200),('jason','female',48,201),('sean',38,('tank',28,202),('oscar',('mac',204)
;
# 查看表结构和数据
MysqL> desc department;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
MysqL> desc employee;
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| dep_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
MysqL> select * from department;
+------+--------------+
| id | name |
+------+--------------+
| 200 | 技术 |
| 201 | 人力资源 |
| 202 | 销售 |
| 203 | 运营 |
+------+--------------+
MysqL> select * from employee;
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
表department与employee
二、多表连接查询
重点:外链接语法
SELECT 字段列表
FROM 表1 INNER|LEFT|RIGHT JOIN 表2
ON 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
2.1 交叉连接
不适用任何匹配条件。生成笛卡尔积
MysqL> select * from employee,department;
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 | 202 | 销售 |
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 | 203 | 运营 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 | 202 | 销售 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 | 203 | 运营 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 | 200 | 技术 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 | 202 | 销售 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 | 203 | 运营 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 | 200 | 技术 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 | 203 | 运营 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 | 202 | 销售 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 | 203 | 运营 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 | 200 | 技术 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 | 202 | 销售 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 | 203 | 运营 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
2.2 内连接
只连接匹配的行
# 找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果
# department没有204这个部门,因而employee表中关于204这条员工信息没有匹配出来
MysqL> select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+
| id | name | age | sex | name |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | nick | 18 | male | 技术 |
| 2 | jason | 48 | female | 人力资源 |
| 3 | sean | 38 | male | 人力资源 |
| 4 | tank | 28 | female | 销售 |
| 5 | oscar | 18 | male | 技术 |
+----+-----------+------+--------+--------------+
# 上述sql等同于
MysqL> select employee.id,department.name from employee,department where employee.dep_id=department.id;
2.3 外链接之左连接
优先显示左表全部记录
# 以左表为准,即找出所有员工信息,当然包括没有部门的员工
# 本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的结果
MysqL> select employee.id,department.name as depart_name from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+------------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+----+------------+--------------+
| 1 | nick | 技术 |
| 5 | oscar | 技术 |
| 2 | jason | 人力资源 |
| 3 | sean | 人力资源 |
| 4 | tank | 销售 |
| 6 | mac | NULL |
+----+------------+--------------+
2.4 外链接之右连接
优先显示右表全部记录
# 以右表为准,即找出所有部门信息,包括没有员工的部门
# 本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加右边有左边没有的结果
MysqL> select employee.id,department.name as depart_name from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+------+-----------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+------+-----------+--------------+
| 1 | nick | 技术 |
| 2 | jason | 人力资源 |
| 3 | sean | 人力资源 |
| 4 | tank | 销售 |
| 5 | oscar | 技术 |
| NULL | NULL | 运营 |
+------+-----------+--------------+
2.5 全外连接
显示左右两个表全部记录
全外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的和右边有左边没有的结果
# 注意:MysqL不支持全外连接 full JOIN
# 强调:MysqL可以使用此种方式间接实现全外连接
select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id
union
select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id
;
# 查看结果
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 203 | 运营 |
+------+------------+--------+------+--------+------+--------------+
# 注意 union与union all的区别:union会去掉相同的纪录
2.6 符合条件连接查询
# 示例1:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25,即找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门
select employee.name,department.name from employee inner join department
on employee.dep_id = department.id
where age > 25;
# 示例2:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示
select employee.id,department
where employee.dep_id = department.id
and age > 25
order by age asc;
三、子查询
- 子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
- 内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
- 子查询中可以包含. IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
- 还可以包含比较运算符. = 、 !=、> 、<等
3.1 带IN关键字的子查询
# 查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
select id,name from department
where id in
(select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25);
# 查看技术部员工姓名
select name from employee
where dep_id in
(select id from department where name='技术');
# 查看不足1人的部门名(子查询得到的是有人的部门id)
select name from department where id not in (select distinct dep_id from employee);
3.2 带比较运算符的子查询
# 比较运算符:=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<>
# 查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄
MysqL> select name,age from emp where age > (select avg(age) from emp);
+---------+------+
| name | age |
+---------+------+
| jason | 48 |
| sean | 38 |
+---------+------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄
select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1
inner join
(select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2
on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id
where t1.age > t2.avg_age;
3.3 带EXISTS关键字的子查询
EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。
而是返回一个真假值。True或False
当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询。
# department表中存在dept_id=203,Ture
MysqL> select * from employee
-> where exists
-> (select id from department where id=200);
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
| 1 | nick | male | 18 | 200 |
| 2 | jason | female | 48 | 201 |
| 3 | sean | male | 38 | 201 |
| 4 | tank | female | 28 | 202 |
| 5 | oscar | male | 18 | 200 |
| 6 | mac | female | 18 | 204 |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+
# department表中存在dept_id=205,False
MysqL> select * from employee
-> where exists
-> (select id from department where id=204);
Empty set (0.00 sec)
四、练习:查询每个部门最新入职的那位员工
4.1 表与数据准备
company.employee
员工id id int
姓名 emp_name varchar
性别 sex enum
年龄 age int
入职日期 hire_date date
岗位 post varchar
职位描述 post_comment varchar
薪水 salary double
办公室 office int
部门编号 depart_id int
# 创建表
create table employee(
id int not null unique auto_increment,name varchar(20) not null,# 大部分是男的
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,hire_date date not null,post varchar(50),post_comment varchar(100),salary double(15,2),office int,# 一个部门一个屋子
depart_id int
);
# 查看表结构
MysqL> desc employee;
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('male','female') | NO | | male | |
| age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 28 | |
| hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | |
| post | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| post_comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
| salary | double(15,2) | YES | | NULL | |
| office | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| depart_id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
# 插入记录
# 三个部门:教学,销售,运营
insert into employee(name,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values
('nick','20170301','老男孩上海虹桥最帅',7300.33,401,1),# 以下是教学部
('jason',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,81,'20130305',8300,73,'20140701',3500,'20121101',2100,'20110211',9000,('rocky','19000301',30000,('成龙','20101111',10000,('歪歪','20150311','sale',3000.13,402,# 以下是销售部门
('丫丫','20101101',2000.35,('丁丁','20110312',1000.37,('星星','20160513',3000.29,('格格','20170127',4000.33,('张野','20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3),# 以下是运营部门
('程咬金','19970312',20000,('程咬银','20130311',19000,('程咬铜','20150411',18000,('程咬铁','20140512',17000,3)
;
# ps:如果在windows系统中,插入中文字符,select的结果为空白,可以将所有字符编码统一设置成gbk
4.2 答案一(连表查询)
SELECT
*
FROM
emp AS t1
INNER JOIN (
SELECT
post,max(hire_date) max_date
FROM
emp
GROUP BY
post
) AS t2 ON t1.post = t2.post
WHERE
t1.hire_date = t2.max_date;
4.3 答案二(子查询)
MysqL> select (select t2.name from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post;
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| (select t2.name from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 张野 |
| 格格 |
| jason |
| nick |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select (select t2.id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post;
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| (select t2.id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 14 |
| 13 |
| 2 |
| 1 |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 正确答案
MysqL> select t3.name,t3.post,t3.hire_date from emp as t3 where id in (select (select id from emp as t2 where t2.post=t1.post order by hire_date desc limit 1) from emp as t1 group by post);
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
| name | post | hire_date |
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
| nick | 老男孩上海虹桥最帅 | 2017-03-01 |
| jason | teacher | 2015-03-02 |
| 格格 | sale | 2017-01-27 |
| 张野 | operation | 2016-03-11 |
+--------+-----------------------------------------+------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
答案一为正确答案,答案二中的limit 1有问题(每个部门可能有>1个为同一时间入职的新员工),我只是想用该例子来说明可以在select后使用子查询。
可以基于上述方法解决:比如某网站在全国各个市都有站点,每个站点一条数据,想取每个省下最新的那一条市的网站质量信息。
五、综合练习
5.1 init.sql文件内容
/*
数据导入:
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : localhost
Source Server Type : MysqL
Source Server Version : 50624
Source Host : localhost
Source Database : sqlexam
Target Server Type : MysqL
Target Server Version : 50624
File Encoding : utf-8
Date: 10/21/2016 06:46:46 AM
*/
SET NAMES utf8;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `class`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `class`;
CREATE TABLE `class` (
`cid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`caption` varchar(32) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`cid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of `class`
-- ----------------------------
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO `class` VALUES ('1','三年二班'),('2','三年三班'),('3','一年二班'),('4','二年九班');
COMMIT;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `course`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `course`;
CREATE TABLE `course` (
`cid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`cname` varchar(32) NOT NULL,`teacher_id` int(11) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`cid`),KEY `fk_course_teacher` (`teacher_id`),CONSTRAINT `fk_course_teacher` FOREIGN KEY (`teacher_id`) REFERENCES `teacher` (`tid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of `course`
-- ----------------------------
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES ('1','生物','1'),'物理','2'),'体育','3'),'美术','2');
COMMIT;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `score`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `score`;
CREATE TABLE `score` (
`sid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`student_id` int(11) NOT NULL,`course_id` int(11) NOT NULL,`num` int(11) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`sid`),KEY `fk_score_student` (`student_id`),KEY `fk_score_course` (`course_id`),CONSTRAINT `fk_score_course` FOREIGN KEY (`course_id`) REFERENCES `course` (`cid`),CONSTRAINT `fk_score_student` FOREIGN KEY (`student_id`) REFERENCES `student` (`sid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=53 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of `score`
-- ----------------------------
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES ('1','1','10'),'2','9'),('5','4','66'),('6','8'),('8','3','68'),('9','99'),('10','77'),('11',('12','87'),('13',('14','79'),('15','11'),('16','67'),('17','100'),('18','5',('19',('20',('21',('22','6',('23',('24',('25',('26','7',('27',('28',('29','88'),('30','8',('31',('32',('33',('34','9','91'),('35',('36',('37','22'),('38','10','90'),('39',('40','43'),('41',('42','11',('43',('44',('45',('46','12',('47',('48',('49',('52','13','87');
COMMIT;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `student`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`sid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`gender` char(1) NOT NULL,`class_id` int(11) NOT NULL,`sname` varchar(32) NOT NULL,KEY `fk_class` (`class_id`),CONSTRAINT `fk_class` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`cid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=17 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of `student`
-- ----------------------------
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('1','男','理解'),'女','钢蛋'),'张三'),'张一'),'张二'),'张四'),('7','铁锤'),'李三'),'李一'),'李二'),'李四'),'如花'),'刘三'),'刘一'),'刘二'),'刘四');
COMMIT;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `teacher`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `teacher`;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`tname` varchar(32) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`tid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of `teacher`
-- ----------------------------
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('1','张磊老师'),'李平老师'),'刘海燕老师'),'朱云海老师'),'李杰老师');
COMMIT;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
5.2 从init.sql文件中导入数据
# 准备表、记录
MysqL> create database db1;
MysqL> use db1;
MysqL> source /root/init.sql
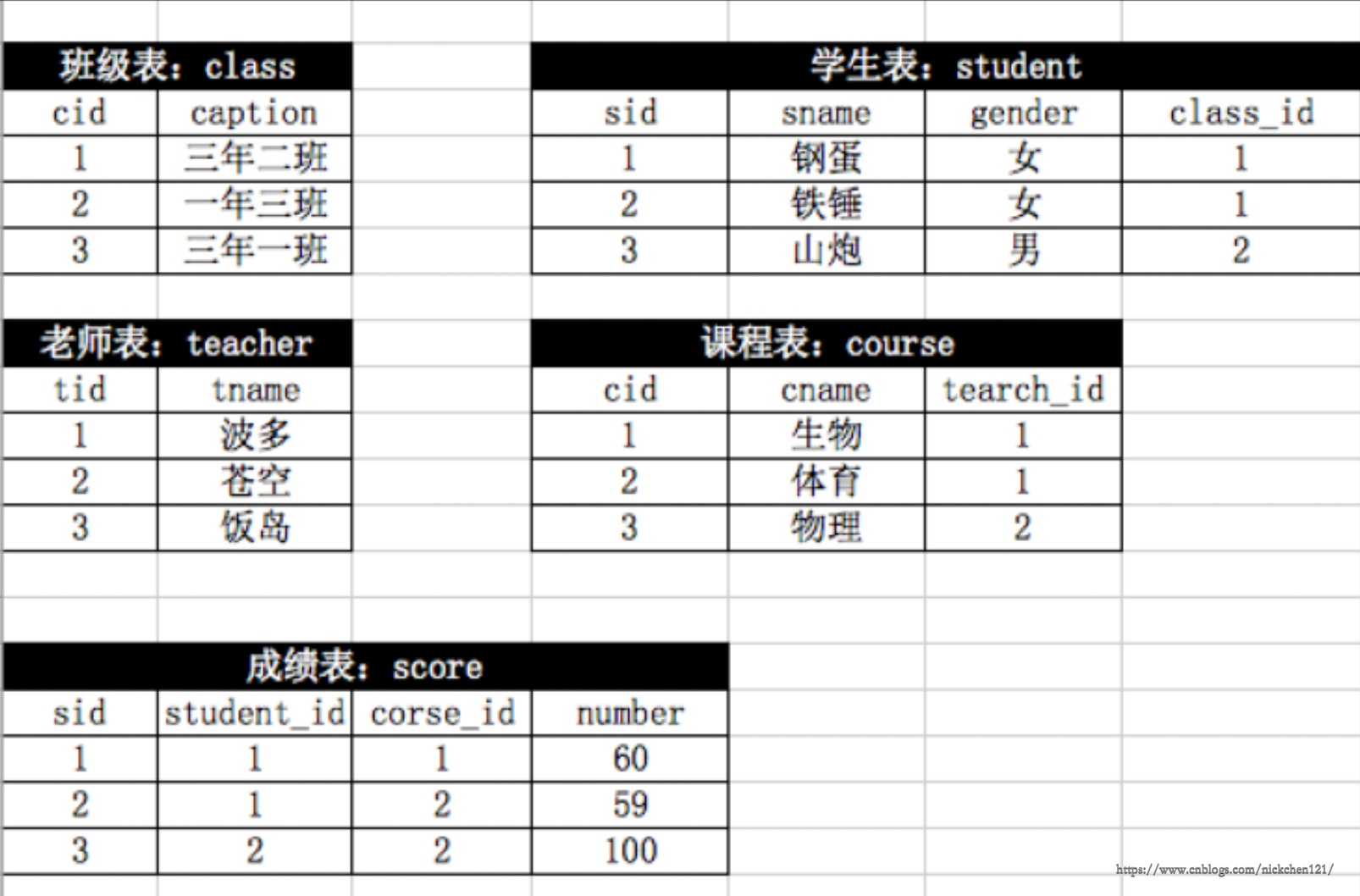
5.3 基础练习
-
查询男生、女生的人数;
-
查询姓“张”的学生名单;
-
课程平均分从高到低显示
-
查询有课程成绩小于60分的同学的学号、姓名;
-
查询至少有一门课与学号为1的同学所学课程相同的同学的学号和姓名;
-
查询出只选修了一门课程的全部学生的学号和姓名;
-
查询课程编号“2”的成绩比课程编号“1”课程低的所有同学的学号、姓名;
-
查询“生物”课程比“物理”课程成绩高的所有学生的学号;
-
查询平均成绩大于60分的同学的学号和平均成绩;
-
查询所有同学的学号、姓名、选课数、总成绩;
-
查询姓“李”的老师的个数;
-
查询没学过“张磊老师”课的同学的学号、姓名;
-
查询学过“1”并且也学过编号“2”课程的同学的学号、姓名;
-
查询学过“李平老师”所教的所有课的同学的学号、姓名;
5.4 进阶练习
- 查询没有学全所有课的同学的学号、姓名;
- 查询和“002”号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学学号和姓名;
- 删除学习“叶平”老师课的SC表记录;
- 向SC表中插入一些记录,这些记录要求符合以下条件:①没有上过编号“002”课程的同学学号;②插入“002”号课程的平均成绩;
- 按平均成绩从低到高显示所有学生的“语文”、“数学”、“英语”三门的课程成绩,按如下形式显示: 学生ID,语文,数学,英语,有效课程数,有效平均分;
- 查询各科成绩最高和最低的分:以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分;
- 按各科平均成绩从低到高和及格率的百分数从高到低顺序;
- 查询各科成绩前三名的记录:(不考虑成绩并列情况)
- 查询每门课程被选修的学生数;
- 查询同名同姓学生名单,并统计同名人数;
- 查询每门课程的平均成绩,结果按平均成绩升序排列,平均成绩相同时,按课程号降序排列;
- 查询平均成绩大于85的所有学生的学号. 姓名和平均成绩;
- 查询课程名称为“数学”,且分数低于60的学生姓名和分数;
- 查询课程编号为003且课程成绩在80分以上的学生的学号和姓名;
- 求选了课程的学生人数
- 查询选修“杨艳”老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生姓名及其成绩;
- 查询各个课程及相应的选修人数;
- 查询不同课程但成绩相同的学生的学号、课程号、学生成绩;
- 查询每门课程成绩最好的前两名;
- 检索至少选修两门课程的学生学号;
- 查询全部学生都选修的课程的课程号和课程名;
- 查询没学过“叶平”老师讲授的任一门课程的学生姓名;
- 查询两门以上不及格课程的同学的学号及其平均成绩;
- 检索“004”课程分数小于60,按分数降序排列的同学学号;
- 删除“002”同学的“001”课程的成绩;
