1. 抛砖引入
《Logstash》
《Filebeat》
《Kibana》
2. 前言
2.1. 现状
以前,查看日志都是通过SSH客户端登服务器去看,使用较多的命令就是 less 或者 tail。如果服务部署了好几台,就要分别登录到这几台机器上看,还要注意日志打印的时间(比如,有可能一个操作过来产生好的日志,这些日志还不是在同一台机器上,此时就需要根据时间的先后顺序推断用户的操作行为,就要在这些机器上来回切换)。而且,搜索的时候不方便,必须对vi,less这样的命令很熟悉,还容易看花了眼。为了简化日志检索的操作,可以将日志收集并索引,这样方便多了,用过Lucene的人应该知道,这种检索效率是很高的。基本上每个互联网公司都会有自己的日志管理平台和监控平台(比如,Zabbix),无论是自己搭建的,还是用的阿里云这样的云服务提供的,反正肯定有。下面,我们利用ELK搭建一个相对真实的日志管理平台。
2.2. 日志格式
我们的日志,现在是这样的:
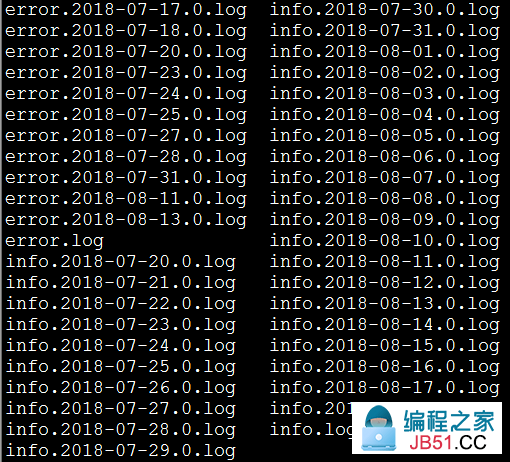
每条日志的格式,类似于这样:
2018-08-22 00:34:51.952 [INFO ] [org.springframework.kafka.KafkaListenerEndpointContainer#0-1-C-1] [com.cjs.handler.MessageHandler][39] - 监听到注册事件消息:
2.3. logback.xml
2.4. 环境介绍
在本例中,各个系统的日志都在/data/logs/${projectName},比如:
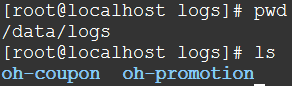
Filebeat,Logstash,Elasticsearch,Kibana都在一台虚拟机上,而且都是单实例,而且没有别的中间件

由于,日志每天都会归档,且实时日志都是输出在info.log或者error.log中,所以Filebeat采集的时候只需要监视这两个文件即可。
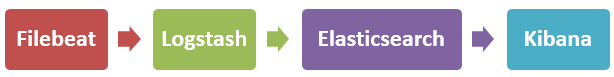
3. Filebeat配置
Filebeat的主要配置在于filebeat.yml配置文件中的 filebeat.inputs 和 output.logstash 区域:
#=========================== Filebeat inputs ============================= filebeat.inputs: - type: log enabled: true # 要抓取的文件路径 paths: - /data/logs/oh-coupon/info.log - /data/logs/oh-coupon/error.log # 添加额外的字段 fields: log_source: oh-coupon fields_under_root: true # 多行处理 # 不以"yyyy-MM-dd"这种日期开始的行与前一行合并 multiline.pattern: ^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2} multiline.negate: true multiline.match: after # 5秒钟扫描一次以检查文件更新 scan_frequency: 5s # 如果文件1小时都没有更新,则关闭文件句柄 close_inactive: 1h # 忽略24小时前的文件 #ignore_older: 24h - type: log enabled: true paths: - /data/logs/oh-promotion/info.log - /data/logs/oh-promotion/error.log fields: log_source: oh-promotion fields_under_root: true multiline.pattern: ^\d{4}-\d{1,2} multiline.negate: true multiline.match: after scan_frequency: 5s close_inactive: 1h ignore_older: 24h #================================ Outputs ===================================== #-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------ #output.elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. #protocol: "https" #username: "elastic" #password: "changeme" #----------------------------- Logstash output -------------------------------- output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Optional SSL. By default is off. # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for SSL client authentication #ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key"
4. Logstash配置
4.1. logstash.yml
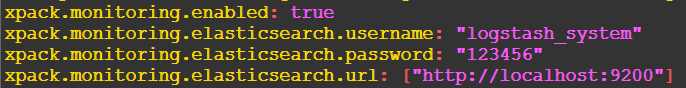
# X-Pack Monitoring # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/monitoring-logstash.html xpack.monitoring.enabled: true xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: "logstash_system" xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: "123456" xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.url: ["http://localhost:9200"]
4.2. 管道配置
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:log_date}\s+\[%{LOGLEVEL:log_level}" }
}
date {
match => ["log_date","yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"]
target => "@timestamp"
}
}
output {
if [log_source] == "oh-coupon" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "localhost:9200" ]
index => "oh-coupon-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "logstash_internal"
password => "123456"
}
}
if [log_source] == "oh-promotion" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "localhost:9200" ]
index => "oh-promotion-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "logstash_internal"
password => "123456"
}
}
}

4.3. 插件
关于Logstash的插件在之前的文章中未曾提及,因为都是配置,所以不打算再单独写一篇了,这里稍微重点的提一下,下面几篇文章对此特别有帮助:
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/input-plugins.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-inputs-beats.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-inputs-kafka.html
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filebeat-modules.html
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/logstash-config-for-filebeat-modules.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html
本例中,到了输入插件:beats,过滤插件:grok和date,输出插件:elasticsearch
这里,最最重要的是 grok ,利用这个插件我们可以从消息中提取一些我们想要的字段
grok
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-filters-grok.html
https://github.com/logstash-plugins/logstash-patterns-core/blob/master/patterns/grok-patterns
date
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-filters-date.html#plugins-filters-date-target
字段引用
@H_301_174@https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/event-dependent-configuration.html#logstash-config-field-references
5. Elasticsearch配置
5.1. elasticsearch.yml
xpack.security.enabled: true
其它均为默认
6. Kibana配置
6.1. kibana.yml
server.port: 5601 server.host: "192.168.101.5" elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200" kibana.index: ".kibana" elasticsearch.username: "kibana" elasticsearch.password: "123456" xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.encryptionKey: "4297f44b13955235245b2497399d7a93"
7. 启动服务
7.1. 启动Elasticsearch
[root@localhost ~]# su - cheng [cheng@localhost ~]$ cd $ES_HOME [cheng@localhost elasticsearch-6.3.2]$ bin/elasticsearch
7.2. 启动Kibana
[cheng@localhost kibana-6.3.2-linux-x86_64]$ bin/kibana
7.3. 启动Logstash
[root@localhost logstash-6.3.2]# bin/logstash -f second-pipeline.conf --config.test_and_exit [root@localhost logstash-6.3.2]# bin/logstash -f second-pipeline.conf --config.reload.automatic
7.4. 启动Filebeat
[root@localhost filebeat-6.3.2-linux-x86_64]# rm -f data/registry [root@localhost filebeat-6.3.2-linux-x86_64]# ./filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml -d "publish"
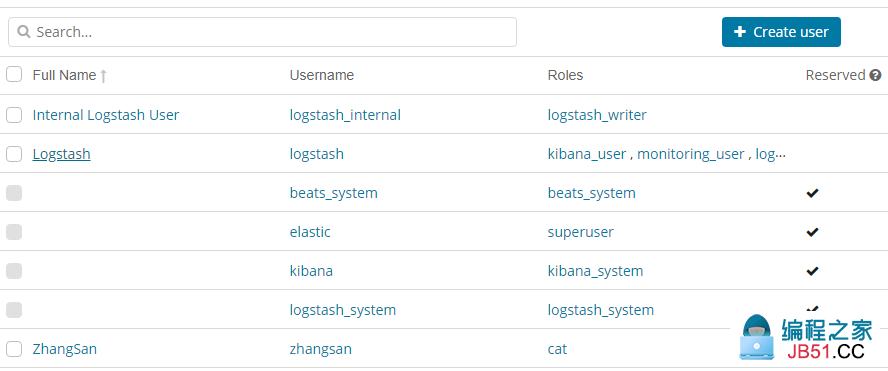
8. 演示



9. 参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/liuxinan/p/5336971.html
原文链接:/elasticsearch/882736.html

